2017 Research
January
Large herbivore browsing leads to above-ground compensatory growth for some species of Acacia trees, but strength and variation of the relationship are poorly understood. Acacia tortilis is a keystone species in East African savannas and experiences a wide range of browsing pressure. In this study, terminal bud scale scars were used to measure yearly shoot elongation in A. tortilis experiencing various levels of elephant browsing at three mesic sites in northern Tarangire National Park, Tanzania.
February
March
With the growing number of antibiotic-resistant pathogens, there is a need for new antibiotics. Bacteria within the order Actinomycetales produce the majority of known antibiotic compounds but harbor cryptic secondary metabolic pathways that likely produce thousands more antibiotics awaiting discovery. This has recently renewed interests in bioprospecting for novel Actinomycetales in underexplored environments, such as the lower atmosphere, and activating cryptic secondary metabolic pathways in previously characterized members of this order.
Understanding bacterial translation is of interest to many high school and college biology students, but hands-on research of this process has traditionally been inaccessible because of the expertise required for molecular cloning. There is also a need for more and better translational control elements that can be used for genetic circuits with applications in medicine, biotechnology, bioremediation, and biomaterials.
April
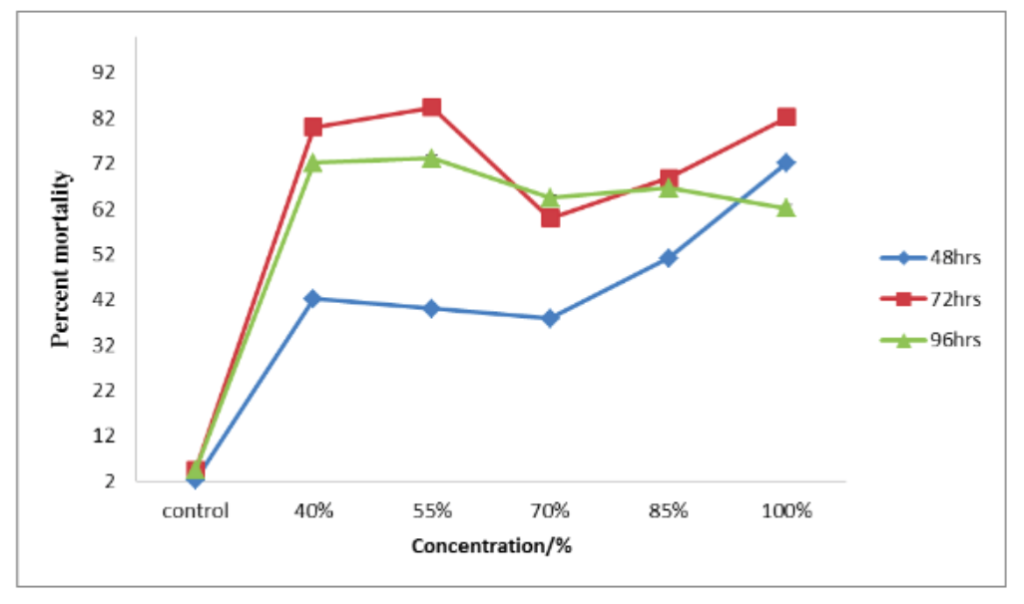
Cowpea aphids (Aphis craccivora) are a major pest of cowpeas (Vigna unguiculata), which feed on the plant at the vegetative stage by sucking the sap. In an endeavour to find an new method of controlling aphid infestation in the Northern Ghana, an in vitro study was carried out to investigate the effect of different concentrations of aqueous false yam (Icacina oliviformis) tuber extract against cowpea black aphids (Aphis craccivora Koch).
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the leading cause of ocular infections in those who wear contact lenses. Others have previously done a study using the antioxidant selenium-coated contact lenses to inhibit the bacteria in an animal model. However, selenium is very toxic even in small quantities. In this study, green tea which is known for its antioxidant property was used to treat contact lenses.
May
June
Recent studies highlight the health risks associated with toxic metal(loid)s [e.g., arsenic (As), zinc (Zn), and lead (Pb)] in dust from mining operations, urban settings, and rural roads. To have a deleterious health effect, inhaled or ingested metal(loid)s must dissolve under conditions in the lung or gastrointestinal tract. In this study, we determined total and physiologically-soluble fractions of metal(loid)s in road dust from four sites in east-central interior Alaska. Total As and antimony (Sb) were enriched up to 26.2 and 53.7, respectively, in dusts relative to average crustal abundance. Several elements such as nickel (Ni), As, and Sb were highly to moderately soluble in simulated lung fluids (7-80%, 15-51%, and 5-42%, respectively). Nickel and As exceeded the EPA inhalation risk unit, which is an exposure level of minimal risk. Despite several elements being highly soluble in simulated gastric fluids, including Ni, copper (Cu), As, and Pb, only As samples exceeded the oral reference dose for children (based on total elemental concentrations) in some samples. The highest exposure risks identified in this study are inhalation of As and Ni present in road dust and ingestion of As-containing dust, especially by children. Additional studies would be needed to further quantify the health risk posed by road dust in this region.
This study investigates the effects of varying sugars and sugar concentrations on the in vitro germination and tube growth of pollens of Cassia alata L., a known Philippine ornamental and medicinal plant. This aims to add information on the pollination fertilization mechanism of the plant for its possible extensive cultivation.
Lyme disease is the most common vector-borne disease in the United States and is typically caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. Although often curable, delayed diagnosis due to nonspecific symptoms risks systemic complications, and some patients experience symptoms despite bacterial clearance from the body. We hypothesized that B. burgdorferi infection induces a self-perpetuating cascade of immunological responses such that symptoms remain after infection or causes residual damage to patients’ immune system and tissues.
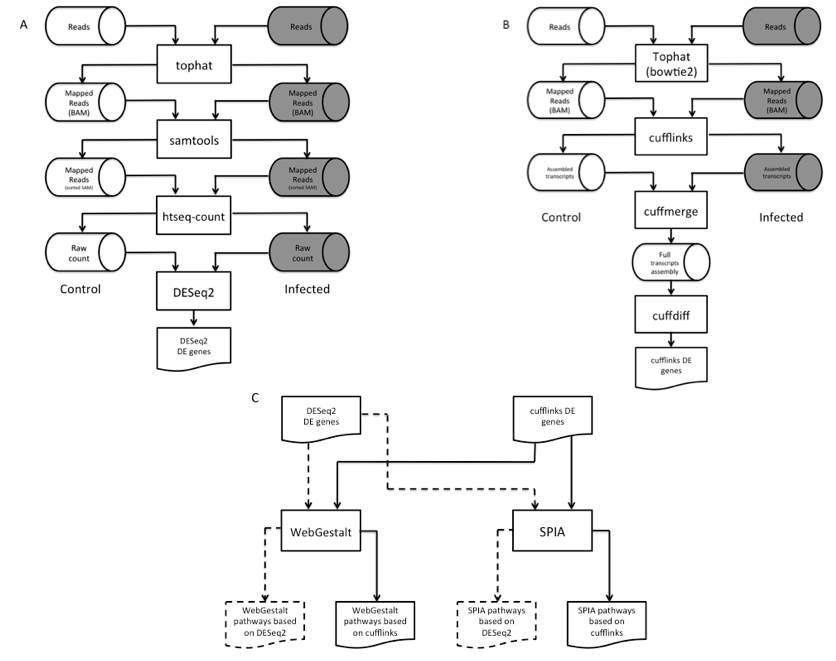
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) classifies antibiotics as a contaminant of emerging concern (CEC) because they are detected in the environment at higher than expected levels and may negatively impact human and aquatic ecosystems (USEPA, 2013). The risk these antibiotics pose to humans and aquatic life is not known; however, the primary concern is that the antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria will develop. Utilization in human healthcare and livestock care are the two main sources of antibiotics in the environment
July
Dehydration from diarrhea leads to a loss of vital electrolytes in the body. The prevalence of electrolytes deficiency and its outcomes due to diarrhea among children under five in Mwanza, Tanzania was not clearly known, thus this study was performed to determine this statistic. A cohort study was conducted among 66 children less than five years old suffering from diarrhea attended and admitted to health centers in Mwanza, Tanzania.
August
Medical imaging is key for the successful diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors, but the initial detection of tumors is, by nature, difficult. Image segmentation, a technique often used to aid detection, is highly dependent on the resolution of the segmented image. Many common morphological segmentation methods often suffer from a lack of resolution which hinders tumor detection. Thus, in this paper, two tumor segmentation techniques are developed and compared using MATLAB – one based on morphological processing, and a second which combines the discrete wavelet transform with morphological processing. Both proposed approaches begin with skull stripping via binary erosion, followed by image contrast enhancement and histogram thresholding.
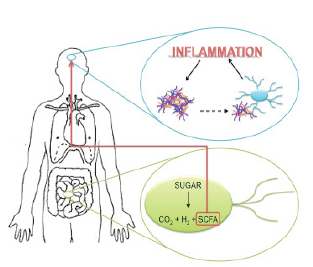
Exploration into the microbial role within behavior and neurologic regulation has been an area of growing interest and research. While in-vitro and in-vivo experimentation has suggested that commensal microbiota play a role within behavioral and neurologic functioning, little distinction has been made about the specific microbes inducing change. In order to understand and potentially utilize this complex gut-microbe-brain connection, it is imperative to distinguish between which microbes are inducing behavioral and or neurologic effects, and which biologic mechanisms are mediating said effects. To enhance the current understanding of neurologically influential microbes, this review will analyze eight microbial strains belonging to the genus types Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, and note the similarities and dissimilarities pertaining to modulation of inflammatory response, intestinal permeability, neurochemical concentrations, and interaction with the vagus nerve expressed amongst included microbial strains.
September
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that has been linked to the incidence of repetitive mild traumatic brain injuries. As chronic traumatic encephalopathy has no formal diagnosis or treatment, current research is striving to better understand its neuropathology in order to develop effective diagnostic and treatment strategies. This review will outline recent research findings in the understanding of the neuropathological mechanisms of chronic traumatic encephalopathy, and connect these findings to advancements in the diagnosis and treatment of the disease. With the emergence of more sophisticated technology, neuroimaging techniques have shown promise as prospective diagnostic tools.
We spend approximately 90% of our time within a built environment, whether it is in our homes, offices, schools, city parks, or public spaces. This bears significance, as we are equally shaped by both our genetic makeup as well as our environment, which brings into question of how we experience space, and in turn how these experiences impact our behaviour. To gain a greater understanding of these impacts, neuroscience seeks to root out the principles of biological mechanisms involved in consciousness, spatial navigation and environmental stressors. However, the use of these principles is not discussed extensively within the curriculum of undergraduate or graduate architecture programs in North America.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic neuroautoimmune condition characterized by neurodegeneration and demyelination throughout the central nervous system. While the pathology of MS is largely unknown, its symptoms are well defined. Current MS therapies such as intravenous corticoid injection, disease modifying treatments (DMTs) and neuro-rehabilitation exist; however most are ineffective as they do not manage symptoms efficeiently, leading to many adverse side effects. Optogenetic stimulation of demyelinated regions may serve as the needed therapy to effectively treat symptoms given the advances achieved in its rapid mechanisms and accurate cell-type-specific delivery strategies. In fact, the hallmark of optogenetic technology is the fast and accurate activation of specific neurons. Current evidence supports optogenetics as a means of controlling or enhancing neural circuitry involved in specific symptoms.
In 2016, Ecuador and Italy both experienced deadly earthquakes, with death tolls of over 800 people even with a commonly used earthquake prediction system in place. The seismometer system, which is the current system used in earthquake prediction, provided no help or warning of the devastating earthquakes that occurred. This method only looks at patterns of previous earthquakes to give the probability of an aftershock once the first earthquake occurs. Newer methods currently being studied look at physical changes in the earth and atmosphere caused by tectonic plate shifting which begin before the main event of an earthquake. In this paper, we will review the use of ionosphere electron measurements, changes in water chemistry, pre-seismic tremors, magnetic field changes, and changes in air chemistry, in the field of earthquake prediction and discuss why combining multiple methods can create a more accurate way of making pre-disaster predictions.
This review outlines an unconventional but timely formulation of quantum dynamics of systems in contact with an environment. This alternative approach to traditional quantum mechanics is generic and is currently gaining attention in a number of fields as, for example, quantum scattering and transport, optical waveguides, devices embedded in an environment, oscillatory classical systems, RLC circuits and other open systems with loss and gain. Here we briefly outline this formulation in which the condition of space-time reflection (PT-symmetry) plays a central role. If PT-symmetry is broken upon parametric change, real energy levels generally turn complex. At the onset of such a symmetry breaking levels coalesce at “Exceptional Points” (EP).
Gastrointestinal dysfunction has a high prevalence in the preclinical phase of Parkinson’s Disease. This review analyzes recent reports that show abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract of Parkinson’s patients compared to controls, suggesting that the disease originates in the gut. The enteric nervous system, which is composed of myenteric and submucosal plexuses, is susceptible to degeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Evidence regarding Parkinsonian-related loss of myenteric dopamine neurons in the outer plexus of the enteric
nervous system is currently controversial.
October
Humans have a unique capacity for higher order cognition such as planning and multitasking. These abilities are collectively referred to as executive functions. This study investigates cognitive set-shifting, a type of executive function that involves shifting from one task to another. Advances in neuroimaging have allowed for the structural integrity of specific frontal lobe subregions to be probed with greater resolution. One such measure is the intensity contrast between cortical gray and white matter, with greater contrast indicating better development.
Seasonal floodplain wetlands occur throughout the Piedmont Region of South Carolina, providing a plethora of ecosystem services. As a result of extensive soil erosion during the agricultural period from mid-1700s until mid-1900s, Piedmont floodplains have accreted significantly, altering their natural flood regime. The purpose of this study was to better understand the impacts of land use change and seasonality on the hydrology of two adjacent, seasonal floodplain wetlands.
November
This paper explores the relationship between the Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual and Transgender movement and the United States Government in Washington, District of Columbia. It makes the argument that the LGBT movement has established itself in the political spatialities found in Washington D.C. in order to create pro-equality social reform. The paper identifies a new trend in the LGBT movement whereby the movement uses networks to manoeuvre in political spaces and places to bring about political change.
December
Recent advances in both the biological and computer sciences have spurred researchers to pay greater attention to the role of computa-tional methods in the broad sphere of cancer research. Specific focus has been given to the demonstrated benefits of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning approaches when compared to current methods for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. An artificial neural network is a form of AI based on algorithms that mimic human brain function. Neural networks are especially useful in the interpretation of nonlinear data, which is commonly encountered in biological research studies. Neural networking technologies may be used to diag-nose cancer more easily and effectively than traditional methods as they decrease the need for invasive procedures and interpreting the results of imaging methods. Additionally, neural networks have been trained to analyze individual prognoses and treatment plans with an accuracy comparable to that of experienced physicians. Advances such as these aid both medical professionals and patients in making optimal health care decisions. As large-scale computing initiatives – such as the recent Microsoft project aiming to “solve” cancer with computer science – move forward, it has become increasingly apparent that the future of medical research will involve technologies such as neural networking and other forms of AI.














A large obstacle on the path to better understanding the evolution of the Universe is knowing the extent to which “nature” and “nurture” affect structures in our Universe. Recent studies have observed that many galactic properties such as luminosity and morphology are dependent on their environment and in particular, their halos, from the galactic cluster scale down to galaxy groups. In this study, we investigate the relationship between dark matter (as a fraction of the total mass of the galaxy) and morphology of individual galaxies to determine if a similar relationship between galaxies and their environment exists at this scale. Our approach differs in the sense that we look at the proportion rather than the actual value of the characteristic we are studying to control for the size of the galaxies.